Long-term value stock investing is an investment strategy that focuses on identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and holding them for the long term. This approach has been proven to generate superior returns over time, making it a popular choice for investors seeking long-term growth.
Key characteristics of long-term value stocks include strong financial performance, low valuations, and sustainable competitive advantages. Successful long-term value investors like Warren Buffett and Benjamin Graham have consistently outperformed the market by adhering to these principles.
Overview of Long-Term Value Stock Investing

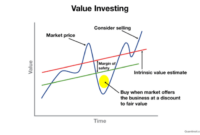
Long-term value stock investing is an investment strategy that focuses on purchasing stocks of companies that are believed to be undervalued relative to their intrinsic value.
The fundamental principle behind this strategy is the belief that over the long term, the stock price of a company will converge to its intrinsic value, which is determined by the company’s fundamentals, such as its earnings, cash flow, and assets.
Long-term value stock investing involves identifying undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and holding them for the long term. Dividend stocks and REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) are two popular investment options within this strategy.
Dividend stocks offer regular income through dividend payments, while REITs provide exposure to the real estate market and offer tax advantages.
Understanding the differences between these options can help investors make informed decisions and maximize their long-term returns.
Key characteristics of long-term value stocks include:
- Strong financial performance, with consistent earnings growth and profitability
- Low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and price-to-book (P/B) ratio, indicating that the stock is trading at a discount to its intrinsic value
- Solid balance sheet with low debt and ample cash flow
- Competitive advantage and strong market position
- Experienced and capable management team
Some successful long-term value investors include Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham, and Peter Lynch. Their strategies have involved identifying companies with strong fundamentals, buying their stocks at a discount to their intrinsic value, and holding them for the long term, allowing the compounding effect of earnings growth to increase their investment returns.
Identifying Long-Term Value Stocks

Identifying long-term value stocks requires a combination of quantitative and qualitative factors:
Quantitative Factors
- Financial statement analysis: Examining financial statements to assess a company’s financial health, profitability, and growth potential
- Valuation techniques: Using valuation models, such as the discounted cash flow (DCF) model, to determine the intrinsic value of a company
Qualitative Factors
- Industry research: Understanding the industry in which a company operates, its competitive landscape, and growth prospects
- Competitive analysis: Evaluating a company’s competitive advantages, market share, and ability to sustain its competitive position
- Management assessment: Assessing the experience, capabilities, and track record of a company’s management team
Portfolio Construction and Management
Constructing a well-diversified long-term value stock portfolio is crucial for managing risk and maximizing returns:
Principles of Portfolio Construction:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different industries, sectors, and company sizes to reduce risk
- Asset allocation: Determining the appropriate mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets based on risk tolerance and investment goals
Managing a Long-Term Value Stock Portfolio:
- Regular monitoring: Tracking portfolio performance and making adjustments as needed
- Rebalancing: Periodically adjusting the portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation
- Tax considerations: Minimizing taxes through strategic investment decisions and tax-advantaged accounts
Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking
Evaluating the performance of long-term value stock investments involves using appropriate metrics:
- Return on investment (ROI): Measuring the total return generated by an investment, including capital appreciation and dividends
- Annualized return: Calculating the average annual return over a specified period
- Sharpe ratio: Assessing the risk-adjusted return of an investment
Benchmarking against industry peers and indices provides context for evaluating performance:
- S&P 500 index: A widely recognized benchmark for large-cap U.S. stocks
- Russell 2000 index: A benchmark for small-cap U.S. stocks
- MSCI World Index: A benchmark for global stocks
Emerging Trends and Challenges
Long-term value stock investing is evolving with emerging trends and challenges:
Emerging Trends, Long-term value stock investing
- ESG integration: Incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions
- Technology advancements: Utilizing data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance investment research and decision-making
Challenges
- Market volatility: Navigating market fluctuations and identifying value opportunities in uncertain environments
- Competition: Adapting to increased competition from other investment strategies, such as growth investing
- Regulatory changes: Understanding and complying with evolving regulatory requirements
End of Discussion
Long-term value stock investing is a disciplined and rewarding investment strategy that requires patience and a deep understanding of fundamental analysis. By identifying undervalued stocks and holding them for the long term, investors can achieve significant wealth creation over time.
FAQ
What are the key principles of long-term value stock investing?
Long-term value stock investing involves identifying undervalued companies with solid fundamentals and holding them for extended periods. While growth stocks can offer explosive returns, they come with higher risk.
By focusing on long-term value, investors aim to mitigate risk and build a portfolio that generates consistent returns over time.
However, it’s important to note that even with long-term value investing, there may be periods of underperformance. However, by diversifying across multiple asset classes, including top performing growth stocks , investors can potentially enhance their overall returns and achieve their long-term financial goals.
The key principles of long-term value stock investing include buying stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value, focusing on companies with strong fundamentals, and holding them for the long term.
How do I identify long-term value stocks?
To identify long-term value stocks, investors can use a combination of quantitative and qualitative factors, such as financial statement analysis, valuation techniques, industry research, and competitive analysis.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in long-term value stock investing?
Long-term value stock investing seeks undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and potential for long-term growth. While this strategy can be rewarding, it’s essential to diversify your portfolio by incorporating growth stocks as well.
Growth stock portfolio diversification involves investing in companies with high growth potential and innovative products or services.
By combining long-term value and growth stocks, you can balance your portfolio and enhance your chances of achieving long-term financial success.
Some common mistakes to avoid in long-term value stock investing include overpaying for stocks, chasing after hot stocks, and selling stocks too early.