How to invest in value stocks – In the realm of investing, value stocks stand out as beacons of opportunity, offering investors the potential for substantial returns. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of value investing, empowering you with the knowledge and strategies to identify, evaluate, and invest in value stocks like a seasoned pro.
As you embark on this journey, you’ll discover the secrets of identifying undervalued companies, building a diversified portfolio, and harnessing the power of patience and discipline. By mastering the art of value investing, you’ll unlock the potential for long-term wealth creation and financial success.
1. Introduction

Value investing is an investment strategy that seeks to purchase stocks of companies that are trading at a price that is significantly below their intrinsic value.
The goal of value investing is to buy stocks at a discount and then hold them for the long term, as the market eventually corrects and the stock price rises to reflect the company’s true value.
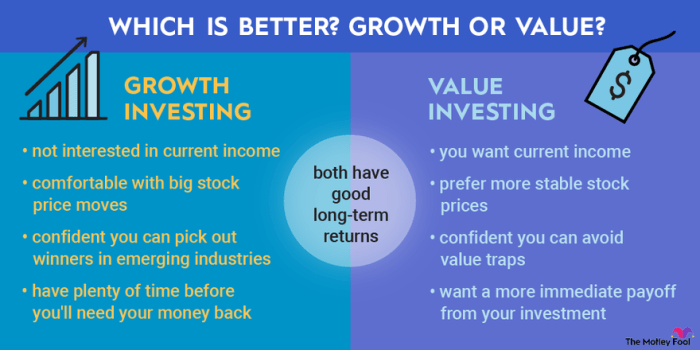
For a more conservative approach, value stocks offer a steady return with less risk. If you’re seeking high-growth potential, consider exploring Top growth stocks in the stock market.
However, it’s important to remember that value stocks still have the potential for long-term growth, especially if you invest in undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
Value investing is an important investment strategy because it can help investors to generate long-term returns that are superior to the market average. Value stocks tend to be less volatile than growth stocks, and they are less likely to be affected by short-term market fluctuations.
There are a number of benefits to value investing, including:
- Reduced risk: Value stocks are less volatile than growth stocks, which means that they are less likely to lose value in a market downturn.
- Higher potential returns: Value stocks have the potential to generate higher returns than growth stocks over the long term.
- Diversification: Value stocks can help to diversify an investment portfolio, which can reduce overall risk.
2. Identifying Value Stocks

There are a number of criteria that can be used to identify value stocks. Some of the most common criteria include:
- Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio): The P/E ratio is a measure of how expensive a stock is relative to its earnings. A low P/E ratio can indicate that a stock is undervalued.
- Price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio): The P/B ratio is a measure of how expensive a stock is relative to its book value. A low P/B ratio can indicate that a stock is undervalued.
- Debt-to-equity ratio: The debt-to-equity ratio is a measure of how much debt a company has relative to its equity. A high debt-to-equity ratio can indicate that a company is financially risky.
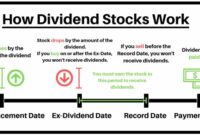
- Dividend yield: The dividend yield is a measure of the amount of dividends that a company pays out to its shareholders relative to its stock price. A high dividend yield can indicate that a stock is undervalued.
In addition to these financial ratios, it is also important to consider the industry in which a company operates when identifying value stocks. Companies in industries that are out of favor with investors may be undervalued, even if they have strong financial fundamentals.
3. Investing in Value Stocks: How To Invest In Value Stocks
There are a number of different strategies that can be used to invest in value stocks. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Buying and holding: This is the most basic value investing strategy. Investors simply buy stocks that they believe are undervalued and then hold them for the long term.
- Value averaging: This strategy involves buying a stock in small increments over time. This can help to reduce the risk of buying a stock at a high price.
- Contrarian investing: This strategy involves buying stocks that are out of favor with investors. This can be a risky strategy, but it can also be very rewarding if the stock price eventually recovers.
It is important to remember that value investing is a long-term investment strategy. It is not a get-rich-quick scheme. Investors who are looking for quick profits should look elsewhere.
4. Evaluating Value Stocks
There are a number of methods that can be used to evaluate the performance of value stocks. Some of the most common methods include:
- Price appreciation: The most obvious way to evaluate the performance of a value stock is to look at its price appreciation. If the stock price has risen significantly since you bought it, then your investment has been successful.
- Dividend yield: The dividend yield is another way to measure the performance of a value stock. A high dividend yield can indicate that the stock is undervalued.
- Total return: The total return of a stock is the sum of its price appreciation and its dividend yield. The total return is a more comprehensive measure of performance than either price appreciation or dividend yield alone.
It is important to note that there is no single “right” way to evaluate the performance of a value stock. The best method will vary depending on your individual investment goals.
5. Case Studies
There are a number of successful value investors who have used this strategy to generate significant wealth. Some of the most famous value investors include:
- Warren Buffett: Buffett is one of the most successful investors of all time. He has used a value investing strategy to generate an annualized return of over 20% for more than 50 years.
- Benjamin Graham: Graham is considered to be the father of value investing. He developed a number of investment principles that are still used by value investors today.
- David Einhorn: Einhorn is a hedge fund manager who has used a value investing strategy to generate significant returns for his investors.
The investment strategies used by these successful value investors vary, but they all share a common goal: to buy stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value.
Final Review
In conclusion, investing in value stocks is a time-tested strategy that has consistently outperformed the broader market over the long term. By understanding the principles of value investing,
implementing sound investment strategies, and exercising patience and discipline, you can harness the power of undervalued companies and achieve your financial goals.
Remember, value investing is not a get-rich-quick scheme. It requires a disciplined approach, a keen eye for undervalued opportunities, and the willingness to stay the course.
By embracing these principles, you’ll be well-positioned to reap the rewards of value investing and build a robust investment portfolio that stands the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is value investing?
Value investing is an investment strategy that focuses on identifying and investing in undervalued stocks that have the potential to generate superior returns over the long term.
Understanding the principles of value investing is crucial before delving into the world of growth stocks. Value stocks represent undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, while growth stocks focus on businesses with high growth potential.
To make informed decisions, it’s essential to consider both value and growth strategies.
For those seeking a deep dive into the best growth stocks available, the article ” Best growth stocks to buy now ” provides valuable insights and recommendations. By combining knowledge of value investing with the analysis of growth stocks, investors can develop a comprehensive investment strategy that aligns with their financial goals.
How do I identify value stocks?
Investing in value stocks can be a smart way to build wealth over time. However, it’s important to do your research and understand the risks involved. One way to reduce your risk is to invest in dividend-paying stocks.
Dividend-paying stocks provide a regular stream of income, which can help to offset any losses you may experience in the stock market.
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are a type of dividend-paying stock that can provide investors with a high yield. REITs invest in real estate, such as apartments, office buildings, and shopping centers.
They are required to pay out at least 90% of their taxable income in dividends, which makes them a good option for investors looking for income.
To identify value stocks, you can use financial ratios such as price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book (P/B), and price-to-sales (P/S). You can also consider industry analysis to identify sectors or companies that are undervalued relative to their peers.
What are the benefits of value investing?
Value investing offers several benefits, including the potential for superior returns over the long term, reduced risk compared to growth investing, and the opportunity to invest in undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.