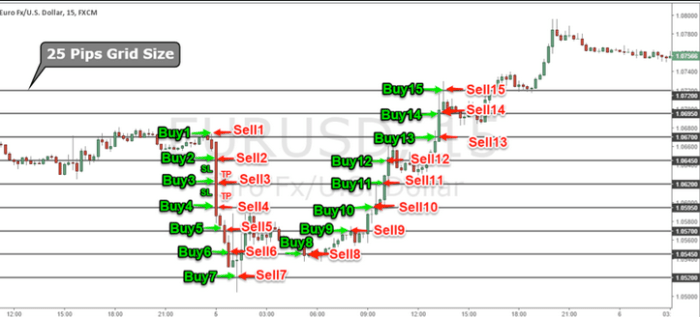
Forex grid trading – is a popular strategy in the foreign exchange market that involves placing multiple buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals above and below a set price level. This technique allows traders to capture price movements in any direction, making it particularly useful in ranging or consolidating markets. However, grid trading also presents challenges, including the risk of accumulating losses during volatile or trending conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of Forex grid trading, covering key strategies, risk management, automation options, and performance evaluation, empowering traders with the knowledge to maximize the potential of this approach.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is Forex Grid Trading?
At its core, Forex grid trading is a non-directional strategy that focuses on capturing price fluctuations rather than predicting market trends. The trader places multiple buy and sell orders at different price levels, creating a grid-like pattern. This allows the trader to profit regardless of whether the market moves up or down, as long as it stays within the grid’s range.
- Definition: Forex grid trading is a strategy that involves placing multiple buy and sell orders at predefined price levels, both above and below the current market price, forming a grid structure. Each order is triggered when the price reaches a certain level, allowing traders to profit from market movements in any direction.
- Grid Structure: The grid consists of a series of orders placed at specific intervals (grid spacing) above and below a central price point. Each level can trigger either a buy or sell order, depending on the market’s movement.
Example of Grid Trading
Suppose the EUR/USD is trading at 1.1000. A trader might set a grid with intervals of 10 pips, placing buy orders at 1.1010, 1.1020, and 1.1030, while simultaneously placing sell orders at 1.0990, 1.0980, and 1.0970. As the market moves, the grid executes these trades to capture profits in both directions.
2. Key Components of Forex Grid Trading
Successful grid trading relies on careful planning and management of several key components:
- Grid Spacing: This refers to the distance between each order in the grid. Tight grid spacing (e.g., 5 pips) may lead to frequent order executions, while wider spacing (e.g., 20 pips) may result in fewer trades but potentially larger profit margins.
- Order Size: Determining the size of each order is critical for managing risk. Using a fixed lot size for every trade ensures consistent exposure, while some traders may prefer to adjust order sizes based on volatility or market conditions.
- Take-Profit and Stop-Loss Levels: It’s important to set take-profit levels to lock in gains and stop-loss levels to minimize losses. This ensures that the grid does not become unmanageable in the event of unexpected market movements.
- Market Conditions: Grid trading works best in range-bound markets with low volatility. In highly volatile or trending markets, this strategy can accumulate losses if price movements continuously exceed the grid’s range.
3. Types of Grid Trading Strategies
There are several variations of grid trading, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the different strategies will help traders choose the approach that best fits their trading style and market conditions.
3.1 Fixed Grid Trading
In fixed grid trading, traders set static price levels at which buy and sell orders are placed. These levels remain constant throughout the trading period, regardless of changes in market conditions.
- Advantages:
- Simplicity: Fixed grid trading is easy to implement and requires minimal monitoring.
- Consistency: Traders can capture small price movements consistently, making this strategy suitable for range-bound markets.
- Disadvantages:
- Lack of Adaptability: Fixed grids may struggle during volatile or trending markets, as the orders may not align with rapid price movements.
- Drawdowns: In trending markets, fixed grids can lead to significant drawdowns as losing trades accumulate.
3.2 Dynamic Grid Trading
Dynamic grid trading adjusts the spacing and placement of orders based on market conditions. For example, if volatility increases, the grid may automatically widen the intervals between orders to account for larger price swings.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility: Dynamic grids adapt to changing market conditions, making them more suitable for volatile markets.
- Risk Management: By adjusting order sizes and grid spacing, traders can better manage risk in response to market fluctuations.
- Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Dynamic grids require more sophisticated monitoring and management, which can make them more challenging to implement.
- Automation Required: Dynamic grids are often best suited for automated trading systems, as manually adjusting orders in real-time can be difficult.
3.3 Hybrid Grid Trading
Hybrid grid trading combines elements of both fixed and dynamic strategies. Traders can set predefined levels for part of the grid while allowing the other part to adjust dynamically based on market conditions. This approach offers the simplicity of a fixed grid with the adaptability of a dynamic grid.
- Advantages:
- Balance Between Simplicity and Flexibility: Traders can enjoy the benefits of both fixed and dynamic grids, depending on market conditions.
- Versatility: Hybrid grids are suitable for a wide range of market conditions, from low volatility to trending markets.
- Disadvantages:
- More Management: Hybrid grids may require more active management to ensure the right balance between fixed and dynamic elements.
- Complexity: This strategy can be more complicated to implement than purely fixed or dynamic grids.
4. Benefits and Risks of Forex Grid Trading
Benefits:
- Potential for Consistent Profits: By capturing both upward and downward price movements, grid trading can generate steady profits, especially in range-bound markets.
- Non-Directional Strategy: Since grid trading does not rely on predicting market direction, traders can profit regardless of whether the market moves up or down.
- Diversification: Grid trading involves placing multiple trades across different price levels, reducing the impact of any single trade on overall performance.
Risks:
- High Transaction Costs: The frequent placement of buy and sell orders can lead to higher transaction costs, especially in volatile markets.
- Exposure to Drawdowns: If the market breaks out of the grid’s range, the trader can face significant losses as orders accumulate in the wrong direction.
- Complexity: Managing multiple open positions simultaneously can be complicated, requiring careful monitoring and adjustment.
5. Automating Forex Grid Trading
Automation is a key element in grid trading, as the strategy often requires the execution of multiple trades simultaneously. Many trading platforms offer grid trading tools or Expert Advisors (EAs) that allow traders to automate the process. Automation reduces the risk of human error, ensures timely execution of trades, and allows traders to monitor multiple markets at once.
- Trading Platforms: Popular platforms like MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 offer built-in features that support grid trading. Traders can set predefined grid parameters, and the system will automatically execute trades when certain conditions are met.
- Custom Scripts: For more advanced traders, custom scripts can be developed to implement specific grid trading strategies, including dynamic adjustments based on market conditions.
Advantages of Automation:
- Reduced Emotional Bias: Automated systems eliminate the risk of emotional decision-making, which can lead to poor trade management.
- Increased Efficiency: Automated systems can monitor and execute trades 24/7, ensuring that no opportunities are missed.
Challenges of Automation:
- Over-Optimization: Some traders may over-optimize their grid trading algorithms, making them too reliant on specific historical conditions that may not apply to future market movements.
- Technical Risks: Automation systems can fail due to technical glitches, such as server downtime or internet issues.
6. Evaluating Grid Trading Performance
Evaluating the performance of a grid trading strategy is essential for determining its long-term viability. Traders should regularly analyze their results and make adjustments as needed. Key performance indicators to consider include:
- Win-Loss Ratio: The proportion of profitable trades compared to losing trades.
- Drawdown: The largest peak-to-valley decline in account equity during a grid trading session.
- Profit Factor: The ratio of gross profit to gross loss, providing insight into the overall profitability of the strategy.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: The ratio of potential profit to potential loss for each trade.
Conclusion
Forex grid trading is a versatile and powerful strategy that allows traders to profit from market movements without the need to predict direction. By placing multiple buy and sell orders at various price levels, traders can capture gains in both trending and range-bound markets.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning, risk management, and a deep understanding of market conditions. Whether using fixed, dynamic, or hybrid grid strategies, traders must be prepared to adapt their approach and leverage automation tools to enhance their trading performance.
While grid trading offers the potential for consistent profits, it also carries significant risks, especially during periods of high volatility. Traders must evaluate their risk tolerance, set appropriate grid parameters, and continually assess their performance to succeed in this complex and rewarding strategy.